Notes from Pennsylvania Planning Comprehensive Planning Examination Study Notes 2007
Part One: Planning Theory
I. Planning History
A. Timeline of American Planning History
-
-
- PREPARING FOR A PROFESSION
- FOUNDATIONS FOR A PROFESSION
- BUILDING A PROFESSION
- REFINING THE PROFESSION
-
3. BUILDING A PROFESSION
1930’s: Great Depression & New Deal

1931 National Land Utilization Conference convened in Chicago. Three hundred agricultural experts deliberate on rural recovery programs and natural resource conservation. Conservation & Environment
1932 Federal Home Loan Bank System established to shore up shaky home financing institutions. Housing Event
1932 In Bove v. Donner-Hanna Coke Corp, the Erie County (Buffalo, New York) court ruled that a property owner cannot make use of his property if it creates a material annoyance to his neighbor or if his neighbor’s property or life is materially lessened by the use. Other Legal Action
1932 Reconstruction Finance Corporation established at the outset of the Great Depression to revive economic activity by extending financial aid to failing financial, industrial, and agricultural institutions. Economic Development Event
1933 Franklin D. Roosevelt inaugurated President of the U.S. The New Deal begins with a spate of counter-depression measures.
1933 Home Owners Loan Corporation established to save homeowners facing loss through foreclosure. Housing Event
1933 The National Planning Board established in the Interior Department to assist in the preparation of a comprehensive plan for public works under the direction of Frederick Delano, Charles Merriam, Wesley Mitchell. Its last successor agency, the National Resources Planning Board, was abolished in 1943. Conservation & Environment History of Planning Profession

1933 Civilian Conservation Corps established to provide work for unemployed youth and to conserve nation’s natural resources. Conservation & Environment
1933 Federal Emergency Relief Administration set up under Harry Hopkins to organize relief work in urban and rural areas. Other Legal Action
1933 Tennessee Valley Authority created to provide for unified and multipurpose rehabilitation and redevelopment of the Tennessee Valley, America’s most famous experiment in river-basin planning. Senator George Norris of Nebraska fathered idea, and David Lilienthal was its most effective implementer. Conservation & Environment Regional Planning Event Landmark Laws Economic Development Event

1933 The Agricultural Adjustment Act is passed to regulate agricultural trade practices, production, prices, supply areas (and therefore land use) as a recovery measure.

1399-34 Century of Progress World Expo was held in Chicago, focusing on The interdependence among industry and scientific research.
1934 American Society of Planning Officials founded, an organization for planners, planning commissioners and planning-related public officials. History of Planning Profession
1934 National Housing Act. Established FSLIC for insuring savings deposits and the FHA for insuring individual home mortgages. Housing Event Landmark Laws

1934 Taylor Grazing Act is passed, its purpose to regulate the use of the range in the West for conservation purposes. Conservation & Environment Regional Planning Event Landmark Laws
1934 “Final Report” by the National Planning Board on its first year of existence. Includes a section entitled “A Plan for Planning” and an account of the “Historical Development of Planning in the United States.” The latter views American planning history in the context of U.S. political and economic history. Landmark Publication
1935 Resettlement Administration established under Rexford Tugwell, Roosevelt “braintruster,” to carry out experiments in land reform and population resettlement. This agency built the three Greenbelt towns (Greenbelt, Maryland; Greendale, Wisconsin; Greenhills, Ohio) forerunners of present day New Towns (Columbia, Maryland; Reston, Virginia; etc.) Planned Communities Landmark Laws
1935 Regional Factors in National Planning is published by the National Resources Committee, a landmark in regional planning literature. Landmark Publication Conservation & Environment Regional Planning Event

1935 Soil Conservation Act. Congress moves to make prevention of soil erosion a national responsibility. Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws

1935 The Historic Sites, Buildings and Antiquities Act, a predecessor of the National Historic Preservation Act, passed. Requires the Secretary of the Interior to identify, acquire, and restore qualifying historic sites and properties and calls upon federal agencies to consider preservation needs in their programs and plans. Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws
1935 Social Security Act passed to create a safety net for elderly. Frances Perkins, Secretary of Labor and first woman cabinet member, was a principal promoter. Landmark Laws
1935 Congress authorizes construction of the Grande Coulee Dam in Central Washington State. Finished in 1941, it is the largest concrete structure in the U.S. and the heart of the Columbia Basin Project, a regional plan comparable in its scope to TVA. The project’s purposes are irrigation, electric power generation and flood control in the Pacific Northwest. Economic Development Event Regional Planning Event
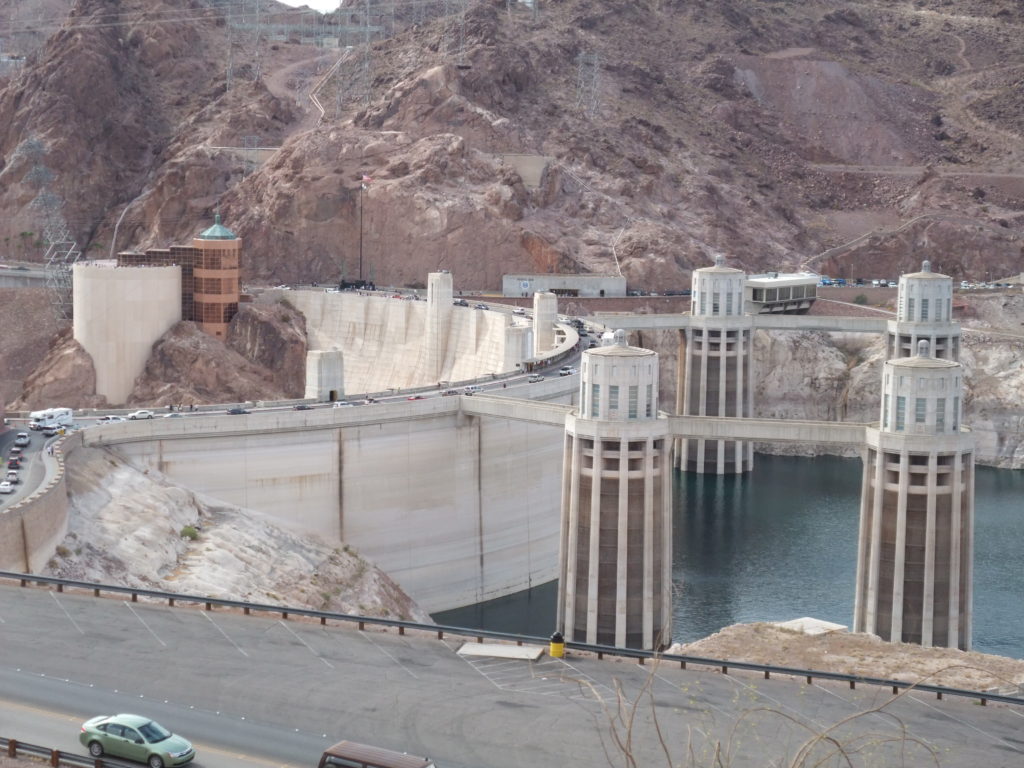

1936 Hoover Dam on the Colorado River completed. Creates and sustains population growth and industrial development in Nevada, California, and Arizona. Economic Development Event Regional Planning Event
1936 Rural Electrification Act provides federal loans for the installation of electrical distribution systems to serve isolated rural areas of the United States. Economic Development Event
1937 Our Cities: Their Role in the National Economy. A landmark report by the Urbanism Committee of the National Resources Committee. (Ladislas Segoe headed research staff.) Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1937 U.S. Housing Act (Wagner-Steagall). Set the stage for future government aid by appropriating $500 million in loans for low-cost housing. Tied slum clearance to public housing. Housing Event Landmark Laws
1937 Farm Security Administration established, successor to the Resettlement Administration and administrator of many programs to aid the rural poor. Landmark Laws
1938 The American Institute of Planners, the planning field’s professional organization, states as its purpose: “… the planning of the unified development of urban communities and their environs, and of states, regions and the nation, as expressed through determination of the comprehensive arrangement of land uses and land occupancy and the regulation thereof.” History of Planning Profession
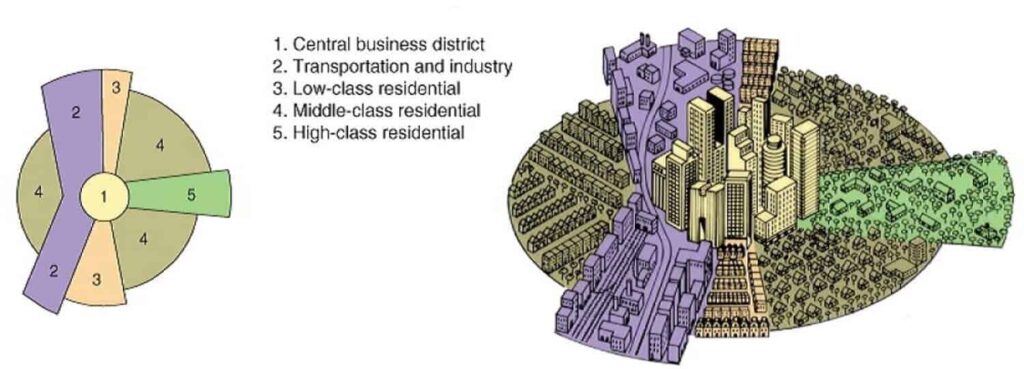
1939 Homer Hoyt’s The Structure and Growth of Residential Neighborhoods in American Cities monograph covers his influential “sector theory” of urban growth. Seminal Publication Housing Event
1941 Ladislas Segoe’s Local Planning Administration, first of “Green Book” series, appears. Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1941 Robert Walker’s Planning Function in Urban Government published. Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1940’s-50’s: World War II & Post-War Boom
1941-44 World War II.
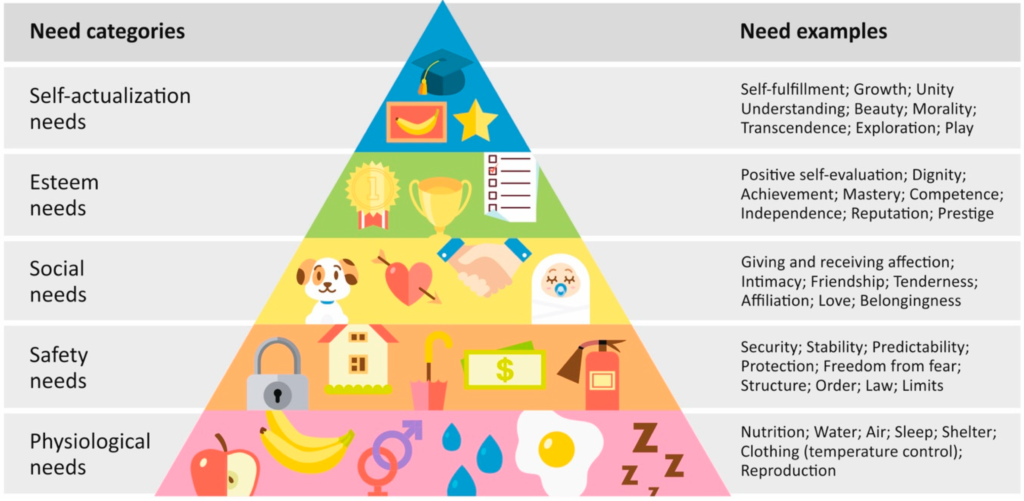
1943 Abraham Maslow’s paper “A Theory of Human Motivation” is published in the journal Psychological Review, including Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The U.S. and allies meet to establish the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (World Bank). Economic Development Event
1944 Serviceman’s Readjustment Act (“G.I. Bill“). Guaranteed loans for homes to veterans under favorable terms, thereby accelerating the growth of suburbs. Housing Event Landmark Laws
1947 Housing and Home Financing Agency (predecessor of HUD) created to coordinate federal government’s various housing programs. Housing Event Landmark Laws
1947 Construction of Park Forest, Illinois, and Levittown, New York, begun as planned suburbs for veterans returning from World War II. Planned Communities
1947 Secretary of State George Marshall proposes the Marshall Plan for the reconstruction of postwar Europe. Economic Development Event Regional Planning Event
1949 Housing Act (Wagner-Ellender-Taft Bill). First U.S. comprehensive housing legislation. Aimed to construct about 800,000 units. Inaugurated urban redevelopment program. Housing Event Landmark Laws

1949 The National Trust for Historic Preservation is created and chartered by Congress. Conservation & Environment
1954 In Berman v. Parker, the U.S. Supreme Court upholds right of Washington, D.C. Redevelopment Land Agency to condemn properties that are unsightly, though non-deteriorated, if required to achieve objectives of duly established area redevelopment plan. U.S. Supreme Court Case Conservation & Environment

1954 In Brown v. Board of Education (Topeka, Kansas), the U.S. Supreme Court states “‘separate but equal’ is inherently unequal,” supporting school integration. U.S. Supreme Court Case
1954 Housing Act of 1954. Stressed slum prevention and urban renewal rather than slum clearance and urban redevelopment as in the 1949 act. Also stimulated general planning for cities under 25,000 population by providing funds under Section 701 of the act. “701 funding” later extended by legislative amendments to foster statewide, interstate, and substate regional planning. History of Planning Profession Regional Planning Event Landmark Laws
1954 Council of Government movement (COGS) begins in the Detroit area with the formation of a Supervisors’ Inter-County Committee composed of the representatives of each county in southeastern Michigan for the purpose of confronting areawide problems. It soon spreads nationwide. Regional Planning Event
1954 Northland Mall in Southfield, Michigan and Southdale Center in Edina, Minnesota are the first totally enclosed shopping centers in the nation. Economic Development Event
1956 Federal Aid Highway Act. Congress passes multibillion dollar act to create Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways (Interstate Highway System) linking all state capitals and most cities of 50,000 population or more. Landmark Laws Economic Development Event

1957 F. Stuart Chapin’s Urban Land Use Planning is published. It explores how to build planning support systems to assess conditions, evaluate policy choices, create visions, and compare scenarios. Seminal Publication
1957 Harvey S. Perloff’s Education for Planning is a landmark, book-length inquiry into the “appropriate intellectual, practical and ‘philosophical’ basis for the education of city and regional planners….” History of Planning Profession Landmark Publication
1959 Kalamazoo, Michigan opens Kalamazoo Mall as the first outdoor pedestrian shopping mall in the United States. Economic Development Event
1959 A. Guttenberg’s “Multiple Land Use Classification System” published in Journal of American Institute of Planners. The first approach to the definition of land-use classifications in multidimensional terms. Landmark Publication
1959 Congress establishes the Advisory Commission on Intergovernmental Relations (ACIR), with members from various branches of government. Serves primarily as a research agency and think tank in area of intergovernmental relations. Landmark Laws Regional Planning Event
1959 The American Collegiate Schools of Planning (ASCP) is born when a few department heads of planning schools get together at the annual ASIP conference to confer on common problems and interests regarding the education of planners. History of Planning Profession

1959 The St. Lawrence Seaway is completed. This joint U.S.-Canada project created, in effect, another American coast, opening the American heartland to seagoing vessels. Economic Development Event Regional Planning Event
1960s: Counterculture & Civil Rights Movement

1960 Kevin Lynch’s Image of the City defines basic elements of city’s “imageability” (paths, nodes, landmarks, edges, and districts) Seminal Publication

1961 Jane Jacobs’s The Death and Life of Great American Cities seminal work includes a critique of planning and planners. Seminal Publication History of Planning Profession
1961 Richard Hedman and Fred Bair publish And On the Eighth Day, a hilarious book of cartoons poking fun at the planning profession by two of our own. Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1961 Hawaii becomes first state to institute statewide zoning. Other Legal Action

1961 A Delaware River Basin Commission representing the states of New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania is created to foster joint management of the river’s water resources. Regional Planning Event
1962 The urban growth simulation model emerges in the Penn-Jersey Transportation Study. Regional Planning Event
1962 Paul Davidoff and Thomas Reiner’s “A Choice Theory of Planning,” seminal article in AIP Journal, lays basis for advocacy planning concept. Seminal Publication
1962 Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring is published and wakes the nation to the deleterious effects of pesticides on animal, plant, and human life. It launches the environmental movement. Landmark Publication Conservation & Environment
1962 Reston, Virginia, a full-scale, self-contained New Town 18 miles from Washington, D.C. is established by the Fairfax County Board of Supervisors as Virginia’s first residential planned community. Planned Communities
1963 Columbia, Maryland, a New Town situated about halfway between Washington and Baltimore, featuring some class integration and the neighborhood principle. Planned Communities
1964 T.J. Kent publishes The Urban General Plan. Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1964 Civil Rights Act outlaws discrimination based on race, creed, and national origin in places of public accommodation. Landmark Laws
1964 Martin Anderson’s The Federal Bulldozer indicts then-current urban renewal program as counterproductive to its professed aims of increased low- and middle income housing supply. With Herbert Gans’s The Urban Villagers (1962), a study of the consequences for community life in a Boston West End Italian-American community, contributes to a change in urban policy. Seminal Publication Housing Event
1964 President Lyndon Johnson declares war on poverty and urges congressional authorization of many remedial programs, plus the establishment of a cabinet-level Department of Housing and Community Development. Economic Development Event
1965 A White House Conference on Natural Beauty in America is convened on May 24 and 25, owing much to the interest and advocacy of the First Lady, Lady Bird Johnson. Conservation & Environment
1965 Housing and urban policy achieve cabinet status when the Housing and Home Finance Agency is succeeded by the Department of Housing and Urban Development. Robert Weaver becomes HUD’s first Secretary and nation’s first African-American cabinet member. Housing Event Landmark Laws
1965 Congress passes the Water Resources Management Act authorizing Federal Multistate river basin commissions. Landmark Laws Regional Planning Event
1965 The Public Work and Economic Development Act passes Congress. This act establishes the Economic Development Administration to extend coordinated, multifaceted aid to lagging regions and foster their redevelopment Economic Development Event Landmark Laws Regional Planning Event
1965 The Appalachian Regional Planning Act establishes a region comprising all of West Virginia and parts of 12 other states, plus a planning commission with the power to frame plans and allocate resources. Economic Development Event Landmark Laws Regional Planning Event
1965 John Reps publishes The Making of Urban America, the first comprehensive history of American urban planning beginning with colonial times. Landmark Publication
1966 The Demonstration Cities and Metropolitan Development Act launched the “model cities” program, an interdisciplinary attack on urban blight and poverty. A centerpiece of President Lyndon Johnson’s “Great Society” program. Housing Event Landmark Laws
1966 With Heritage So Rich, a seminal historic preservation book, is published. Conservation & Environment Seminal Publication

1966 National Historic Preservation Act passed. Establishes the National Register of Historic Places and provides, through its Section 106, for the protection of preservation-worthy sites and properties threatened by federal activities. This act also creates the national Advisory Council on Historic Preservation and directs that each state appoint a State Historic Preservation Officer (SHPO). Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws
1966 The Department of Transportation Act provides protection to parkland, wildlife refuges, and other preservation-worthy resources in building national roads. Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws
1967 The “(Louis B.) Wetmore Amendment” drops the final phrase in the 1938 AIP declaration of purpose which tied it to the comprehensive arrangement and regulation of land use. The effect is to broaden the scope and membership of the profession by including “social planners” as well as “physical planners.” History of Planning Profession
1968 To implement Intergovernmental Relations Act of 1968 the Office of Management and Budget issues Circular A-95 requiring state and substate regional clearinghouses to review and comment on federally assisted projects to facilitate coordination among the three levels of government. Other Legal Action Regional Planning Event
1968 The 8th Circuit rules in Jones v. Mayer that racial barriers cannot affect the acquisition of property. Other Legal Action
1968 Apollo 8‘s The Blue Marble photo of the Earth catalyzes the modern environmental movement. Conservation & Environment
1969 Ian McHarg publishes Design with Nature, tying planning to the natural environment. Seminal Publication
1969 National Environmental Policy Act requires an “environmental impact statement” for every federal or federally aided state or local major action that might significantly harm the environment. Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws
1969 Mel Scott publishes American City Planning Since 1890. Reissued in 1995 by the American Planning Association. Landmark Publication History of Planning Profession
1970’s: Conservative Populism & Social Movements

1970 First “Earth Day” held on January 1. Conservation & Environment
1970 Federal Environment Protection Agency (EPA) established to administer main provisions of the Clean Air Act (1970). Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws Regional Planning Event
1970 The Miami Valley (Ohio) Regional Planning Commission Housing Plan is adopted, the first such plan in the nation to allocate low- and moderate-income housing on a “fair share” basis. Housing Event Regional Planning Event
1971 AIP adopts a Code of Ethics for professional planners. History of Planning Profession
1971 In James v. Valtierra, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld an amendment to the California Constitution mandating a referendum on all housing projects because an intent to racially discriminate could not be found. U.S. Supreme Court Case
1971 In Calvert Cliffs Coordinating Committee v. U.S. Atomic Energy Commission, the U.S. Supreme Court found that an approval for a nuclear power plant was not properly granted because the requirements of the National Environmental Protection Act (NEPA) were not followed. U.S. Supreme Court Case

1972 Coastal Zone Management Act adopted. Conservation & Environment Regional Planning Event Landmark Laws
1972 U.S. State and Local Fiscal Assistance Act inaugurated general revenue sharing. Landmark Laws
1972 In Golden v. Planning Board of Ramapo, New York high court allows the use of performance criteria as a means of slowing community growth. Other Legal Action

1972 Demolition of St. Louis’s notorious Pruitt-Igoe Project symbolizes a nationwide move away from massive, isolating, high-rise structures to a more humane form of public housing architecture: low-rise, less isolated, dispersed. Housing Event
1973 Endangered Species Act. Authorized Federal assistance to state and local jurisdictions to establish conservation programs for endangered plant and animal species. Conservation & Environment Landmark Laws
1973 The Oregon Supreme Court rules in Fasano v. Board of County Commissioners of Washington County that all zoning and rezoning must be consistent with applicable comprehensive plans. Other Legal Action
1974 The Housing and Community Development Act replaces the categorical grant with the block grant as the principal form of federal aid for local community development. Landmark Laws
1974 In Village of Belle Terre v. Boraas, the U.S. Supreme Court rules that limiting residents of housing units to related individuals was a legitimate use of the police power, eliminating many fundamental civil rights challenges to local regulations. U.S. Supreme Court Case Housing Event
1975 The U.S. 4th Circuit finds that quotas on the annual number of building permits issued was a constitutional use of the police power in Sonoma v. Petaluma. Other Legal Action

1975 Cleveland Policy Plan Report shifts emphasis from traditional land-use planning to advocacy planning. It is a pluralistic and inclusive planning theory where planners seek to represent the interests of various groups within society. Seminal Publication History of Planning Profession
1975 The New Jersey Supreme Court rules in Southern Burlington County NAACP v. Township of Mt. Laurel that the local zoning ordinance was unconstitutional where it conflicted with state defined fair housing practices. Other Legal Action Housing Event
1976 In City of Eastlake v. Forest City Enterprises, the U.S. Supreme Court held that a mandate that all rezonings be subject to referendum is constitutional because no intent to discriminate could be found. U.S. Supreme Court Case
1976 In Young v. American Mini Theaters, Inc., the U.S. Supreme Court upheld a zoning provision mandating the decentralization of sexually oriented businesses based on studies showing a detriment to society as a
result of clustering. U.S. Supreme Court Case
1976 The California Supreme Court, in Associated Home Builders of Greater East Bay v. City of Livermore, found that temporary moratoria on building permit issuance was constitutional. Other Legal Action

1976 Historic Preservation Fund established in the NPS to help State (and now Tribal) Historic Preservation Offices to recognize, save, and protect historic places. Conservation & Environment
1977 In Village of Arlington Heights v. Metropolitan Housing Development Corp., the U.S. Supreme Court finds that a regulation effectively denying housing to people based on race, immigration status, or national origin was unconstitutional. Further a regulation effectively denying housing to people based on gender or illegitimacy must substantially advance a legitimate state interest and be passed or enforced with intent to discriminate. U.S. Supreme Court Case Housing Event
1977 First exam for American Institute of Planners (AIP) membership conducted. History of Planning Profession
1978 In Penn Central Transportation Co. v. City of New York, the U.S. Supreme Court upholds New York City’s Landmark Preservation Law as applied to Grand Central Terminal. In this landmark decision, the Court found that barring some development of air rights was not a taking when the interior of the property could be put to lucrative use. U.S. Supreme Court Case
1978 American Institute of Planners (AIP) and American Society of Planning Officials (ASPO) merge to become American Planning Association (APA). History of Planning Profession
-
- PREPARING FOR A PROFESSION
- FOUNDATIONS FOR A PROFESSION
- BUILDING A PROFESSION
- REFINING THE PROFESSION
